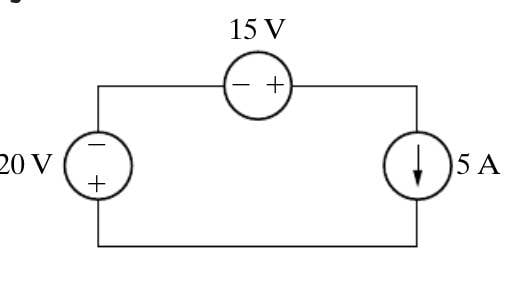
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around determining the voltage polarity of an independent current source in a circuit. Participants explore the implications of voltage polarity on power calculations and the behavior of active versus passive components.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants suggest adding up the voltages around the loop to determine the voltage polarity of the current source.
- One participant reports calculating a voltage of -5 V and questions how to identify the positive and negative ends of the current source's voltage.
- Another participant argues that the polarity of power does not matter, using examples of resistors to illustrate their point.
- Some participants assert that the current source's terminal voltage indicates whether it is delivering or receiving power, referencing real-world examples like a car battery.
- There is a contention regarding the applicability of ideal components in circuit analysis, with some suggesting that ideal models can lead to unrealistic predictions.
- Participants discuss the relationship between voltage, current, and power, noting that while power can have polarity, this relationship can vary with passive components like resistors, inductors, and capacitors.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the significance of voltage polarity in power calculations, with no clear consensus reached. Some argue that polarity is crucial, while others maintain that it does not affect power dissipation in certain contexts.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight limitations in using ideal components for circuit analysis, noting that real-world circuits do not behave like ideal models and can lead to contradictions.