PhysicsTest
- 260
- 27
- Homework Statement
- To understand the current and voltage rating terminology of the inverter.
- Relevant Equations
- NA
I have a great difficulty in understanding the current and voltage ratings of the inverter, at the input of the inverter the ratings are different compared to the output side. What are the formulae of those conversions example,
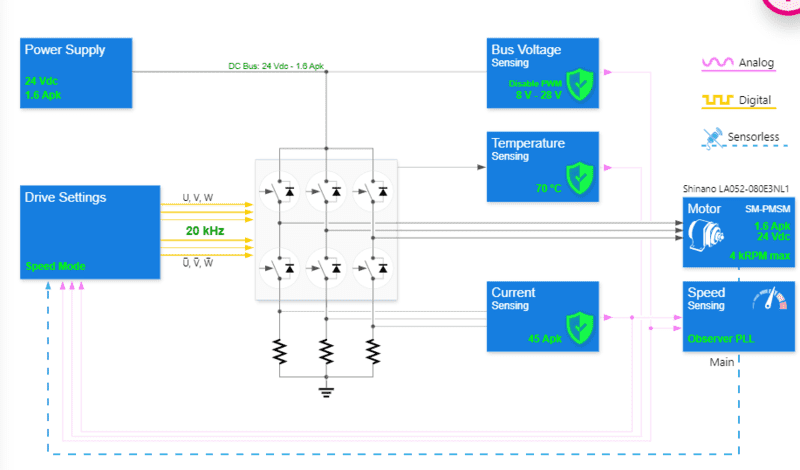
If i check the above diagram, power supply is 24V, 1.6APk
a. Does it mean the inverter is designed for 24*1.6 = 38.4 Watts?
b. Power is constant can the voltage and current can be different to maintain power, ex: 12V, 3.2A pk = 38.4 Watts? Will there be any limitations on that i mean lower limit on voltage?
c. The motor specifications are again the same, so i need to select a motor which meets my power supply requirements or i need to design an inverter for a motor?
d. Most important is in the current sensing it can read upto 45Apk, when my input is only 1.6A pk why it is required to measure on power side of 45A? How much maximum current flows through and what is the equation to derive it? Please advise.
If i check the above diagram, power supply is 24V, 1.6APk
a. Does it mean the inverter is designed for 24*1.6 = 38.4 Watts?
b. Power is constant can the voltage and current can be different to maintain power, ex: 12V, 3.2A pk = 38.4 Watts? Will there be any limitations on that i mean lower limit on voltage?
c. The motor specifications are again the same, so i need to select a motor which meets my power supply requirements or i need to design an inverter for a motor?
d. Most important is in the current sensing it can read upto 45Apk, when my input is only 1.6A pk why it is required to measure on power side of 45A? How much maximum current flows through and what is the equation to derive it? Please advise.