- #1
physicsnoob204
- 4
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- What is the direction of the frictional force in these 3 scenarios?
What is the direction of the frictional forces especially when there are 2 forces acting on an object? (see attached Image)
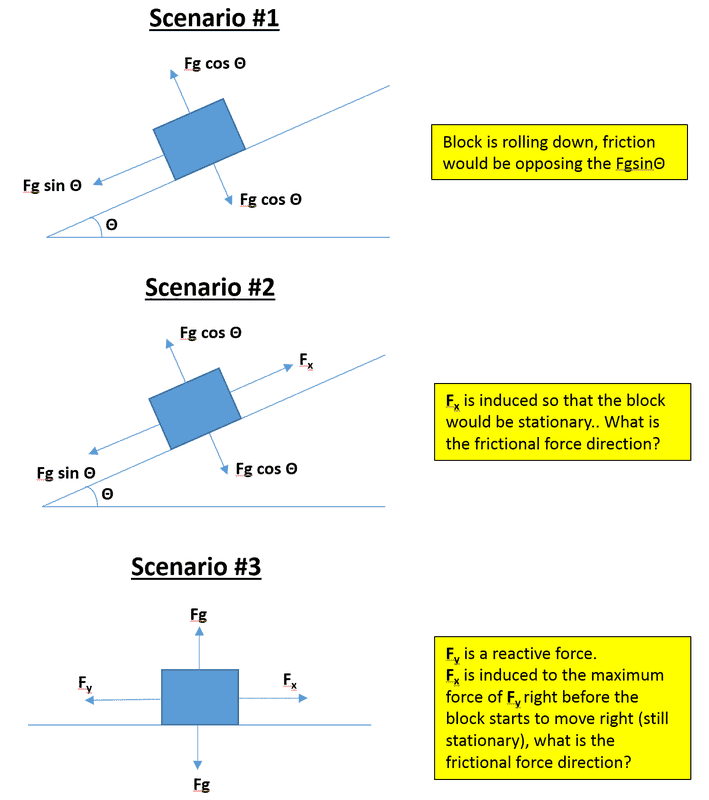
The basic approach is to generalize the equations based on FBD and then solve it.physicsnoob204 said:Summary:: What is the direction of the frictional force in these 3 scenarios?
What is the direction of the frictional forces especially when there are 2 forces acting on an object? (see attached Image)View attachment 264664
The direction of frictional forces on balanced force objects depends on the direction of the applied force. If the applied force is in the same direction as the motion of the object, the frictional force will act in the opposite direction to slow down the motion. If the applied force is in the opposite direction of the motion, the frictional force will act in the same direction to resist the motion.
The magnitude of the frictional force on a balanced force object remains constant as long as the applied force remains constant. However, if the applied force increases, the frictional force will also increase until it reaches its maximum value, known as the limiting friction. If the applied force decreases, the frictional force will also decrease until it becomes zero when the applied force is equal to the limiting friction.
The direction of frictional forces on balanced force objects is affected by the nature of the surfaces in contact, the normal force between the surfaces, and the coefficient of friction. The coefficient of friction is a measure of how rough or smooth the surfaces are, and it determines the strength of the frictional force.
Yes, the direction of frictional forces on balanced force objects can change if the direction of the applied force changes. For example, if the object is moving in a straight line and the applied force suddenly changes direction, the frictional force will also change direction to oppose the new direction of motion.
Frictional forces act in the opposite direction of motion, so they can slow down or stop the motion of a balanced force object. They also help to maintain the stability of an object by preventing it from sliding or slipping. In some cases, frictional forces can also cause an object to start moving in the opposite direction of the applied force.