Homework Help Overview
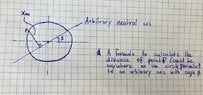
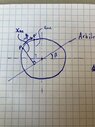
The discussion revolves around formulating an equation for the shortest distance from a point on the perimeter of a circle to an arbitrary axis. The problem involves geometric concepts, specifically relating to circles and angles.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the use of rotation matrices and the implications of rotating points around the origin. There are attempts to clarify how to derive the new coordinates after rotation and the relationship between angles involved.
Discussion Status
Some participants have provided guidance on using rotation and trigonometric relationships to approach the problem. There is an ongoing exploration of the necessary geometric relationships and the completeness of the problem statement, with no explicit consensus reached yet.
Contextual Notes
There are questions regarding the completeness of the problem statement, particularly concerning the radius of the circle and the angle definitions. Participants are also considering the implications of the given angles and their relationships in the context of the problem.