Homework Help Overview
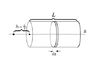
The discussion revolves around determining the electric potential at a point outside a charged cylinder, focusing on the geometry and charge density involved. Participants are examining the separation vector and its components in cylindrical coordinates.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking, Mathematical reasoning
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning the definition of the separation vector in cylindrical coordinates and discussing the geometry of the charge distribution. There are attempts to clarify the radial component and its relation to the overall distance calculation.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants providing insights into the geometry and suggesting that a complete statement of the problem would facilitate better assistance. Some have proposed potential expressions for the distance calculation while others are still seeking clarity on the definitions involved.
Contextual Notes
There is mention of a lack of symmetry in the problem setup, which may affect the approach to finding the electric potential. Participants are also navigating the implications of using cylindrical coordinates versus Cartesian coordinates.