SUMMARY
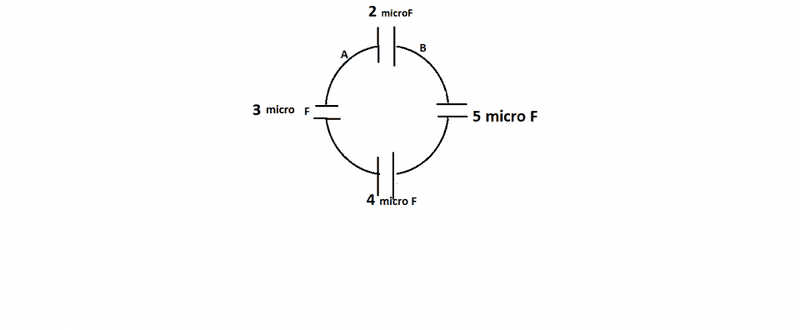
The discussion focuses on determining the equivalent capacitance between two points, A and B, in a circuit with capacitors arranged in a circular configuration. Participants clarify that while some capacitors appear in series, the arrangement can also be interpreted as a mirrored layout, leading to confusion about the connections. The key takeaway is that the equivalent capacitance can be simplified to a single capacitor that represents the entire network between points A and B, regardless of the physical arrangement of the capacitors.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of capacitor configurations: series and parallel connections
- Familiarity with the concept of equivalent capacitance
- Basic knowledge of circuit diagrams and their representations
- Ability to interpret electrical circuit problems and apply relevant equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of formulas for equivalent capacitance in series and parallel configurations
- Learn how to analyze complex circuits using Kirchhoff's laws
- Explore practical applications of capacitors in electronic circuits
- Investigate the impact of capacitor arrangement on overall circuit behavior
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electrical engineering, educators teaching circuit analysis, and hobbyists interested in electronics who want to deepen their understanding of capacitor arrangements and equivalent capacitance calculations.