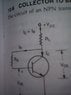
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the concepts of Vceq and Icq in the context of collector-base bias configuration in transistor circuits. Vceq represents the collector-emitter voltage at the quiescent point (Q point), while Icq denotes the collector current at this same operating point. The base resistance (Rb) is calculated using the formula Rb = (Vcc - Vbe - IcRl) / Ib, although an alternative approximation of Rb = Vceq / Ib is also mentioned. The discussion emphasizes the importance of using upper-case subscripts for DC bias points and applying Kirchhoff's voltage law for accurate circuit analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of transistor biasing techniques
- Familiarity with Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL)
- Knowledge of quiescent point (Q point) in transistor circuits
- Basic circuit analysis skills involving resistances and voltages
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of transistor biasing equations in detail
- Learn about the significance of the quiescent point in amplifier design
- Explore the impact of neglecting Vbe in biasing calculations
- Review practical examples of collector-base bias configurations
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, electronics students, and hobbyists interested in transistor circuit design and analysis will benefit from this discussion.