mathmari
Gold Member
MHB
- 4,984
- 7
Hey! 
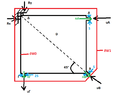
Air of pressure $p_0$ and velocity $|\overrightarrow{u}_{A}|=|\overrightarrow{u}_{B}|=c$ enters the space $D$ from the sections $A, B$ of surface $S$. If at the orifices the distribution of the pressure and the velocity is uniform and at the exit $\Gamma$ the pressure is equal to the atmospheric one $P_a$, find the forces $R_x, R_y$ acting on the support $\Delta$ (air density $\rho_a$).
View attachment 4420
The solution that I found in my notes is the following:
$$\overrightarrow{F}_{W_0}=-\int_{\partial{W_1}}p\overrightarrow{n}dA-\int_{\partial{W_1}}\rho \overrightarrow{u}(\overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{n})dA$$
$\overrightarrow{F}_{W_0}$ is the force over the solid boundary $\partial_{W_0}$ (square ΑΒΓΔ)
Continuity equation: $$u_{\Gamma}S_{\Gamma}=u_AS_A+u_BS_B \Rightarrow u_{\Gamma}2S=cS+cS \Rightarrow u_{\Gamma}=u_A=u_B=c$$
$$\text{ Section } A : \overrightarrow{n}_A=\hat{i} \ \ , \ \ \overrightarrow{u}_{A}=-c\hat{i} \\ \text{ Section } B : \overrightarrow{n}_B=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j}) \ \ , \ \ \overrightarrow{u}_{B}=c\left (-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})\right ) \\ \text{ Section } \Gamma : \overrightarrow{n}_{\Gamma}=-\hat{j} \ \ , \ \ \overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma}=-c\hat{j}$$
$$\overrightarrow{u}_{A} \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{A}=-c \\ \overrightarrow{u}_{B} \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{B}=-c \\ \overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma} \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{\Gamma}=c$$
$$\int_{\partial{W_1}}p\overrightarrow{n}dA=P_AS\hat{i}+P_BS\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})+P_{\Gamma}2S(-\hat{j})=P_0S\left (\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})\right )-2P_aS\hat{j}=P_0S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}-\left (P_0S\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2P_aS\right )\hat{j}$$
$$\int_{\partial{W_1}}\rho \overrightarrow{u}(\overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{n})dA=\rho_a [\overrightarrow{u}_A (\overrightarrow{u}_A \cdot \overrightarrow{n})S_A+\overrightarrow{u}_B (\overrightarrow{u}_B \cdot \overrightarrow{n})S_B+\overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma} (\overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma} \cdot \overrightarrow{n})S_{\Gamma}]=\rho_a [-c\hat{i}(-c)S-c\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})(-c)S-c\hat{j}c2S]=\rho_a c^2S\left (\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})-2\hat{j}\right )=\rho_ac^2S\left (\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}-\left ( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2\right )\hat{j}\right )$$
$$\overrightarrow{F}_{W_0}=-P_0S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}+\left (P_0S\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2P_aS\right )\hat{j}-\rho_a c^2S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}+\rho_a c^2S\left (\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2\right )\hat{j}$$
$$F_{W_0,x}=-\left (P_0+\rho_a c^2\right )S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )<0 \\ F_{W_0, y}=\left (\left ( P_2\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2P_a\right ) +\rho_ac^2\left (\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2\right )\right )S>0$$
Balance of the construction:
$$R_x+F_{W_0, x}=0 \Rightarrow R_x=-F_{W_0, x}>0 \\ -R_y+F_{W_0, y}=0 \Rightarrow R_y=F_{W_0, y}>0$$
How we have we found that $\overrightarrow{n}_B=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})$ ?? (Wondering)
Could also explain to me how we have calculated the integrals $\int_{\partial{W_1}}p\overrightarrow{n}dA$ and $\int_{\partial{W_1}}\rho \overrightarrow{u}(\overrightarrow{u}\cdot \overrightarrow{n})dA$ ?? (Wondering)
Air of pressure $p_0$ and velocity $|\overrightarrow{u}_{A}|=|\overrightarrow{u}_{B}|=c$ enters the space $D$ from the sections $A, B$ of surface $S$. If at the orifices the distribution of the pressure and the velocity is uniform and at the exit $\Gamma$ the pressure is equal to the atmospheric one $P_a$, find the forces $R_x, R_y$ acting on the support $\Delta$ (air density $\rho_a$).
View attachment 4420
The solution that I found in my notes is the following:
$$\overrightarrow{F}_{W_0}=-\int_{\partial{W_1}}p\overrightarrow{n}dA-\int_{\partial{W_1}}\rho \overrightarrow{u}(\overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{n})dA$$
$\overrightarrow{F}_{W_0}$ is the force over the solid boundary $\partial_{W_0}$ (square ΑΒΓΔ)
Continuity equation: $$u_{\Gamma}S_{\Gamma}=u_AS_A+u_BS_B \Rightarrow u_{\Gamma}2S=cS+cS \Rightarrow u_{\Gamma}=u_A=u_B=c$$
$$\text{ Section } A : \overrightarrow{n}_A=\hat{i} \ \ , \ \ \overrightarrow{u}_{A}=-c\hat{i} \\ \text{ Section } B : \overrightarrow{n}_B=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j}) \ \ , \ \ \overrightarrow{u}_{B}=c\left (-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})\right ) \\ \text{ Section } \Gamma : \overrightarrow{n}_{\Gamma}=-\hat{j} \ \ , \ \ \overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma}=-c\hat{j}$$
$$\overrightarrow{u}_{A} \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{A}=-c \\ \overrightarrow{u}_{B} \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{B}=-c \\ \overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma} \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{\Gamma}=c$$
$$\int_{\partial{W_1}}p\overrightarrow{n}dA=P_AS\hat{i}+P_BS\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})+P_{\Gamma}2S(-\hat{j})=P_0S\left (\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})\right )-2P_aS\hat{j}=P_0S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}-\left (P_0S\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2P_aS\right )\hat{j}$$
$$\int_{\partial{W_1}}\rho \overrightarrow{u}(\overrightarrow{u} \cdot \overrightarrow{n})dA=\rho_a [\overrightarrow{u}_A (\overrightarrow{u}_A \cdot \overrightarrow{n})S_A+\overrightarrow{u}_B (\overrightarrow{u}_B \cdot \overrightarrow{n})S_B+\overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma} (\overrightarrow{u}_{\Gamma} \cdot \overrightarrow{n})S_{\Gamma}]=\rho_a [-c\hat{i}(-c)S-c\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})(-c)S-c\hat{j}c2S]=\rho_a c^2S\left (\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})-2\hat{j}\right )=\rho_ac^2S\left (\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}-\left ( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2\right )\hat{j}\right )$$
$$\overrightarrow{F}_{W_0}=-P_0S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}+\left (P_0S\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2P_aS\right )\hat{j}-\rho_a c^2S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )\hat{i}+\rho_a c^2S\left (\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2\right )\hat{j}$$
$$F_{W_0,x}=-\left (P_0+\rho_a c^2\right )S\left (1+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right )<0 \\ F_{W_0, y}=\left (\left ( P_2\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2P_a\right ) +\rho_ac^2\left (\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}+2\right )\right )S>0$$
Balance of the construction:
$$R_x+F_{W_0, x}=0 \Rightarrow R_x=-F_{W_0, x}>0 \\ -R_y+F_{W_0, y}=0 \Rightarrow R_y=F_{W_0, y}>0$$
How we have we found that $\overrightarrow{n}_B=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}(\hat{i}-\hat{j})$ ?? (Wondering)
Could also explain to me how we have calculated the integrals $\int_{\partial{W_1}}p\overrightarrow{n}dA$ and $\int_{\partial{W_1}}\rho \overrightarrow{u}(\overrightarrow{u}\cdot \overrightarrow{n})dA$ ?? (Wondering)
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: