- #1
D.B0004
- 17
- 0
Homework Statement
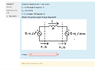
Please see attachment for circuit and parameters.
Homework Equations
i --> 90 phase angle for inductor so Z of inductor = 0.5<90
sum of voltages = 0
#<40 = #*cos(40) + i*sin(40)*#
The Attempt at a Solution
shteii01 - 100 + 0.5<90 + V2<theta = 0 --> 100 + 0.5*cos(90) + i*sin(90)0.5+V2*cos(theta)+i*sin(theta)*V2 = 0 --> two unknowns
OR
delta V = I * Z and then take V1 - delta V to find V2. The work seems simple but I get the wrong answer! Note that the answer I have in the attachment was my first solution which I did in my head - not the one I got from the methods shown above. Thanks for the help.