chwala
Gold Member
- 2,833
- 426
- Homework Statement
- see attached
- Relevant Equations
- integration
Find question here,
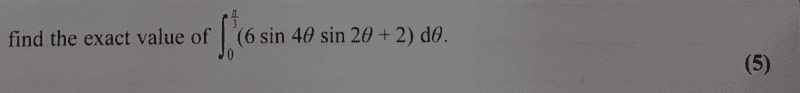
My approach, using cosine sum and product concept, we shall have;
##\cos (A+B)-\cos (A-B)=-2\sin A\sin B##
##⇒\cos D-\cos C=-2\sin\dfrac{C+D}{2} \sin\dfrac {C-D}{-2}##
##⇒-3[\cos(A+B)-\cos(A-B)]=6\sin A sinB##
We are given ##A=4θ## and ##B=2θ##, therefore,
##⇒-3[\cos 6θ-\cos 2θ]=6\sin 4θ\sin2θ##
##⇒3\cos 2θ-3\cos 6θ=6\sin 4θ\sin2θ##
I made use of chain rule in my working... i.e letting ##u=2θ## and ##u=6θ## ...
##\int_0^\frac{π}{3} [3\cos 2θ-3\cos 6θ+2] dθ=\dfrac{3}{2} \sin 2θ-\dfrac{1}{2} \sin 6θ +2θ## from ##[θ=0]## to ##[θ=\frac{π}{3}]##
On substituting the given limits, we end up with,
##[1.2990-0+2.094395]-[0]=3.393## to 3 decimal places...
Any other approach is welcome...cheers
My approach, using cosine sum and product concept, we shall have;
##\cos (A+B)-\cos (A-B)=-2\sin A\sin B##
##⇒\cos D-\cos C=-2\sin\dfrac{C+D}{2} \sin\dfrac {C-D}{-2}##
##⇒-3[\cos(A+B)-\cos(A-B)]=6\sin A sinB##
We are given ##A=4θ## and ##B=2θ##, therefore,
##⇒-3[\cos 6θ-\cos 2θ]=6\sin 4θ\sin2θ##
##⇒3\cos 2θ-3\cos 6θ=6\sin 4θ\sin2θ##
I made use of chain rule in my working... i.e letting ##u=2θ## and ##u=6θ## ...
##\int_0^\frac{π}{3} [3\cos 2θ-3\cos 6θ+2] dθ=\dfrac{3}{2} \sin 2θ-\dfrac{1}{2} \sin 6θ +2θ## from ##[θ=0]## to ##[θ=\frac{π}{3}]##
On substituting the given limits, we end up with,
##[1.2990-0+2.094395]-[0]=3.393## to 3 decimal places...
Any other approach is welcome...cheers
Last edited: