- #1
ick84
- 2
- 0
Homework Statement
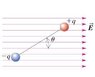
For the dipole shown, the charges are ± 3.0 micro coulombs separated by a distance of 3.20 nm and oriented so that the theta is 35.0 degrees. If the electric field has a magnitude of 8000 N/C, find the magnitude and direction (clockwise/counterclockwise) of the net torque on the dipole about the same axis as before.
Homework Equations
F = qE
torque = Fl
The Attempt at a Solution
first i solved for F = (3.0E-6 C)(8000N/C) = 2.4E-2 N
then solved for l = (3.20nm)(sin35) = 1.84E-9
net torque = 2 * F * l ??