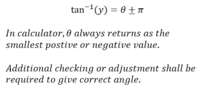SUMMARY
The discussion centers on calculating the magnitude and direction of a vector using the Pythagorean theorem and the inverse tangent function. The magnitude was correctly calculated as √5, while the angle was initially found to be 63.8 degrees using θ = arctan(-2/-1). However, confusion arose regarding the angle's representation on a graph, leading to an incorrect adjustment to 116.6 degrees. The correct approach involves recognizing the quadrant of the vector and applying the appropriate angle adjustments.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vector magnitude calculation using the Pythagorean theorem
- Knowledge of the inverse tangent function (arctan)
- Familiarity with angle measurement in different quadrants
- Basic trigonometric principles related to tangent
NEXT STEPS
- Study vector representation in different quadrants
- Learn about angle adjustments for vectors in the Cartesian plane
- Explore the use of polar coordinates in vector analysis
- Review trigonometric identities and their applications in vector calculations
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics or mathematics, particularly those focusing on vector analysis and trigonometry. This discussion is beneficial for anyone needing to understand vector magnitude and direction calculations.