SUMMARY
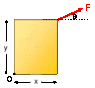
The discussion centers on calculating the magnitude of torque produced by a force of 75.0 N applied at an angle of 35.0° to a box with dimensions 2.51 m by 1.62 m. The correct formula for torque is t = rFsin(θ), where θ is the angle between the radial vector and the direction of the force. Participants emphasize the importance of accurately identifying this angle to apply the formula correctly, as previous calculations at 0° and 90° did not require this consideration.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of torque and its calculation using the formula t = rFsin(θ)
- Knowledge of basic trigonometry, particularly sine functions
- Familiarity with vector representation in physics
- Ability to interpret diagrams and identify angles in physics problems
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of torque in-depth, focusing on the relationship between force, distance, and angle
- Learn how to draw and interpret radial vectors in physics problems
- Practice calculating torque with varying angles using the formula t = rFsin(θ)
- Explore applications of torque in real-world scenarios, such as in mechanical systems
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics, as well as educators looking for examples of torque calculations in applied scenarios.