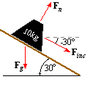
Force normal and force along the incline
Click For Summary
Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the force components acting on a block resting on an inclined plane, specifically the force along the incline ($F_{inc}$) and the normal force ($F_n$). Participants explore the decomposition of gravitational force into orthogonal components and the relationships between these forces in the context of a 30-degree incline.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant states that gravitational force ($F_g$) can be decomposed into two orthogonal vectors, leading to the equation $F_g = F_{inc} - F_n$.
- Another participant suggests that $F_g$ is -98N and proposes a calculation for $F_{inc}$ using the expression $F \langle \cos{60^\circ}, \sin{60^\circ} \rangle$.
- Several participants discuss the geometry of the situation, referencing a 30-60-90 triangle where $F_g$ is the hypotenuse and $F_{inc}$ and $F_n$ are the legs.
- There is a proposal to use sine functions to express $a$ and $b$ in terms of $F_g$, with $a = F_g \sin(30)$ and $b = F_g \sin(60)$.
- One participant claims to have calculated $F_{normal}$ as 84.957N and $F_{inc}$ as 49N, based on their diagram and the relationships derived from the triangle.
- Another participant confirms the calculated values and provides a reasoning based on the angles formed between the forces and the gravitational force.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying methods and interpretations for calculating the forces, with some agreeing on the numerical values while others question the approach and the need for diagrams to clarify the relationships. No consensus is reached on a single method or interpretation.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved aspects regarding the definitions of the forces and the assumptions made in the calculations, particularly concerning the angles and the signs of the components. The discussion also reflects differing interpretations of the geometric relationships involved.
Similar threads
- · Replies 7 ·
- · Replies 20 ·
- · Replies 9 ·
- · Replies 13 ·
- · Replies 3 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 37 ·
- · Replies 5 ·