Plasm47
- 10
- 0
In the graph below, forces labelled positive act in the direction of motion of the object, forces labelled negative oppose the motion. The object under consideration has a mass of 2.0kg and was initially at rest. Calculate its kinetic energy and speed when
a) d= 2.0m
b) d= 4.0m
c) d=6.0m
d) d= 8.0m
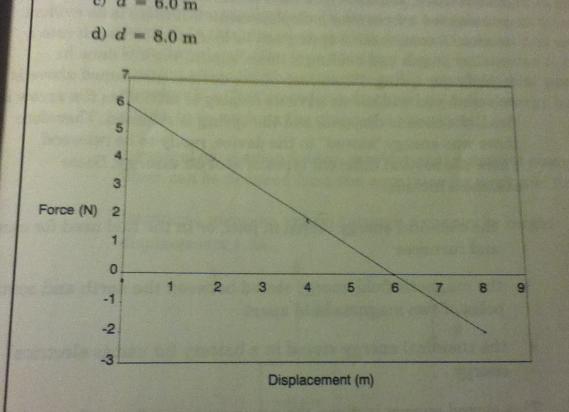
I know W is area under the graph, but not positive how to apply it. I assume the question is only asking for that moment in time, and NOT a time period.
so for (a) it would be W= 4.0N x 2.0m = 8J; which would also be Ek
and V= 2.83m/s
if this is correct then b and c follow the same method, so i got those right aswell.
Not sure of the procedure when the Force is negative.
a) d= 2.0m
b) d= 4.0m
c) d=6.0m
d) d= 8.0m
I know W is area under the graph, but not positive how to apply it. I assume the question is only asking for that moment in time, and NOT a time period.
so for (a) it would be W= 4.0N x 2.0m = 8J; which would also be Ek
and V= 2.83m/s
if this is correct then b and c follow the same method, so i got those right aswell.
Not sure of the procedure when the Force is negative.
Last edited: