- #1
manal950
- 177
- 0
Hi

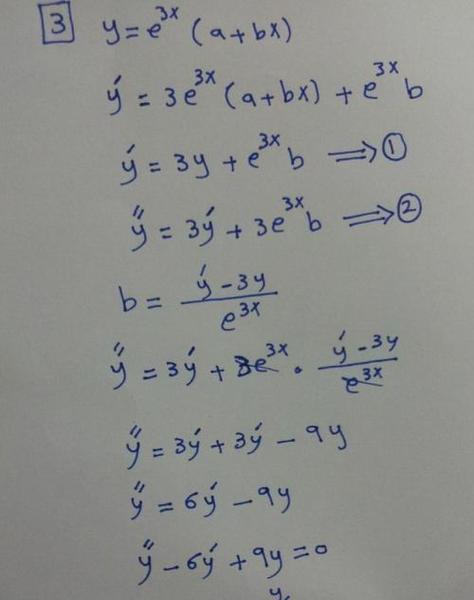
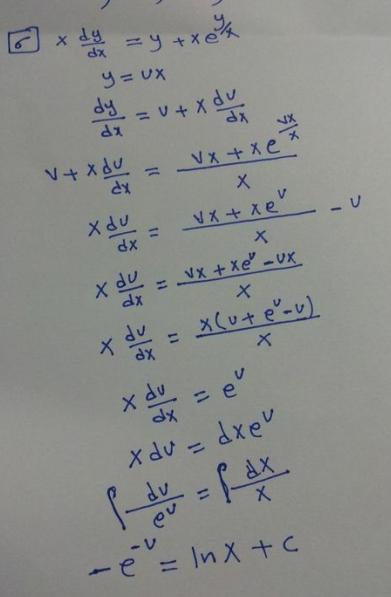
A differential equation is a mathematical equation that describes the relationship between a function and its derivatives. It involves the use of derivatives, which represent the rate of change of a function, to describe the behavior of a system over time.
A differential equation can be formed by identifying the variables and their derivatives in a given system and expressing their relationship as an equation. This can involve using known physical laws, such as Newton's laws of motion, or empirical data from experiments.
An ordinary differential equation (ODE) involves a single independent variable and its derivatives, while a partial differential equation (PDE) involves multiple independent variables and their derivatives. In other words, an ODE describes a function in terms of one variable, while a PDE describes a function in terms of multiple variables.
A differential equation is homogeneous if all of its terms contain the dependent variable and its derivatives, and there are no terms that do not involve the dependent variable. In other words, the equation is "balanced" in terms of the dependent variable and its derivatives.
To solve a homogeneous differential equation, you can use the substitution method, where you substitute a new variable to transform the equation into a separable form. You can also use the method of undetermined coefficients, where you assume a solution form and solve for the coefficients. Another method is variation of parameters, where you assume a solution form and solve for the parameters using a system of equations.