SUMMARY
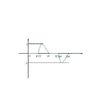
The discussion revolves around sketching a piecewise function defined by f(wt) = 0 for 0 ≤ ωwt ≤ π/2, f(wt) = Vsin(ωt) for π/2 ≤ ωwt ≤ π, f(wt) = 0 for π ≤ ωwt ≤ 3π/2, and f(wt) = Vsin(ωwt) for 3π/2 ≤ ωwt ≤ 2π. Participants emphasize the importance of accurately sketching the waveform, noting that transitions between segments should be vertical. The Fourier series coefficients, particularly a0, are discussed, with participants seeking clarification on integration methods and the implications of the function's symmetry.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of piecewise functions and their graphical representation
- Familiarity with Fourier series and Fourier coefficients
- Knowledge of trigonometric functions, specifically sine functions
- Basic integration techniques for calculating Fourier coefficients
NEXT STEPS
- Study the process of deriving Fourier coefficients for piecewise functions
- Learn about the convolution theorem in relation to Fourier transforms
- Explore the implications of function symmetry on Fourier series
- Practice sketching piecewise functions and identifying their periodic properties
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics and engineering, particularly those focusing on signal processing, waveform analysis, and Fourier analysis.