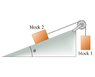
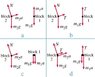
Free-body diagram for two boxes connected on a pulley.
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the proper construction of a free-body diagram for two boxes connected by a pulley on a frictionless plane. Key forces identified include gravity, normal force, and tension, with emphasis on distinguishing "actual" forces from derived quantities like "ma." Participants agree that "ma" is not a force and should not be included in free-body diagrams. The consensus is that actual forces must have identifiable agents, such as gravity exerted by the Earth and tension exerted by the rope.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Newton's Laws of Motion, particularly the first, second, and third laws.
- Familiarity with free-body diagrams and their components.
- Knowledge of forces such as gravity, normal force, and tension.
- Basic principles of mechanics in a frictionless environment.
- Study the construction of free-body diagrams in various mechanical systems.
- Learn about the implications of Newton's Laws in real-world applications.
- Explore the concept of tension in strings and ropes in physics problems.
- Investigate the differences between contact forces and long-range forces.
Students of physics, educators teaching mechanics, and anyone involved in engineering or physical sciences who seeks to understand force interactions in systems involving pulleys and free-body diagrams.
Similar threads
- · Replies 22 ·
- · Replies 34 ·
- · Replies 17 ·
- · Replies 22 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 18 ·
- · Replies 24 ·
- · Replies 2 ·