Jose Antonio
- 3
- 0
Hello everyone, this is my first post so I don't know whether or not this is the right thread to be asking this question (if so I am sorry). I am currently working on my thesis where I am determining the thickness of a GaN crystal through second harmonic generation. However in a article published by J. Jerphagnon and S. K. Kurtz, they defined a Fresnel-like transmission coefficient for the second harmonic signal as:
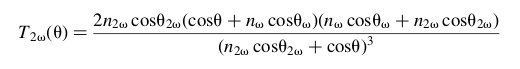
I was wondering if anyone knew a source of how to get this result. I am intrigued on why this transmission coefficient is not the absolute value squared (since it is a capital T) since one could be considering the complex form of the refractive indices. Thanks in advance for any response!
I was wondering if anyone knew a source of how to get this result. I am intrigued on why this transmission coefficient is not the absolute value squared (since it is a capital T) since one could be considering the complex form of the refractive indices. Thanks in advance for any response!