SUMMARY
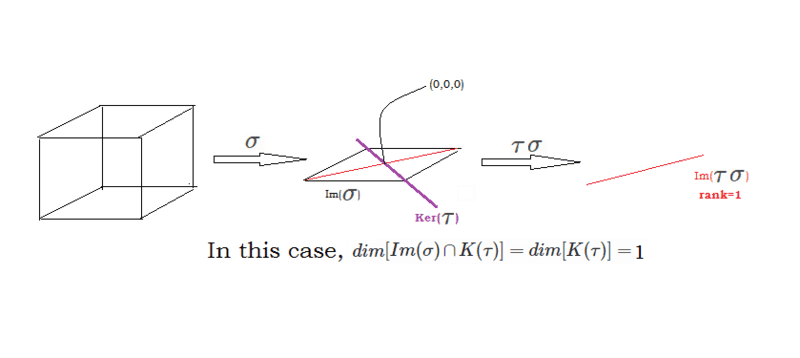
The discussion centers on the geometric intuition behind the rank formula for linear transformations, specifically the equation ##\rho(\tau)=\rho(\tau\sigma)+d[Im(\sigma)\cap K(\tau)]##. Participants analyze the implications of projecting a 3D object onto 2D and 1D spaces, emphasizing that such projections result in a loss of information and a decrease in rank. The conversation highlights the importance of understanding projectors and their properties, particularly in relation to linear independence and the kernel of transformations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of linear transformations and their ranks
- Familiarity with the concepts of image and kernel in linear algebra
- Knowledge of projection operators and their properties
- Basic comprehension of geometric representations in algebra
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of projection operators in linear algebra
- Explore the geometric interpretation of rank in linear transformations
- Learn about the implications of dimensionality reduction in data representation
- Investigate applications of rank in discrete mathematics and data analysis
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, students of linear algebra, data scientists, and anyone interested in the geometric interpretation of mathematical concepts related to rank and transformations.