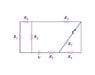
- #1
mathnoobie
- 63
- 0
Homework Statement
I really just need help understanding how to re-draw a resistor diagram after calculating an equivalent resistor.
Now in the picture given in the attachment, you can see that R1 and R6 are in series with each other
when I compute their equivalent resistor(R1+R6), on what location on the system of resistors would I place the equivalent resistor? Would I place it in the location of R1, R6, or some intermediate point in between? I know that no matter which of the three choices I pick, it'll still be in parallel with R2 but I'm just looking for clarity in the expected placement.