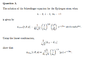SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on solving the Schrödinger equation using polar coordinates, specifically addressing the conversion of polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates and the application of linear combinations of wavefunctions. Participants emphasize the importance of first adding the wavefunctions and then simplifying the result using Euler's formula. The conversation highlights the significance of understanding the notation related to d orbitals, particularly the values of m (+1 and -1) associated with l = 2. Ultimately, the contributor successfully solves the problem after initial confusion, demonstrating the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of polar coordinates and their conversion to Cartesian coordinates
- Familiarity with the Schrödinger equation and quantum mechanics concepts
- Knowledge of linear combinations of wavefunctions
- Proficiency in using Euler's formula for simplifying exponential expressions
NEXT STEPS
- Research the application of linear combinations in quantum mechanics
- Study the properties and significance of d orbitals in quantum chemistry
- Learn about the mathematical techniques for converting between coordinate systems
- Explore advanced topics in quantum mechanics related to wavefunction interactions
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in quantum mechanics, physicists working with wavefunctions, and anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of the Schrödinger equation in polar coordinates.