SUMMARY
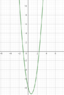
The discussion centers on the function f(x) = 3x² - 4x - 8 and its zeros, specifically how they relate to the integral of the function. The zeros of the function are found to be a = -2, 0, and 4, derived from the equation a³ + 2a² + 8a = 0. The integral from -2 to 0 and from 0 to 4 both yield an area of zero, indicating that the areas above and below the x-axis cancel each other out. This relationship emphasizes the importance of understanding the zeros when analyzing the integral of a function.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of polynomial functions and their zeros
- Knowledge of definite integrals and area under the curve
- Familiarity with graphing quadratic functions
- Basic algebra skills for solving equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- Learn how to compute definite integrals for polynomial functions
- Explore the graphical interpretation of integrals and areas
- Investigate the relationship between a function's zeros and its integral
USEFUL FOR
Students studying calculus, particularly those focusing on integrals and polynomial functions, as well as educators looking for examples of teaching integral concepts through graphical analysis.