WWCY
- 476
- 15
Homework Statement
Hi all, I'm working on the following problem and would like some help. Many thanks in advance!
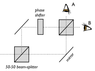
The Figure below presents the Mach-Zehnder interferometer with an additional phase shift element in the upper path.
$$\left( \begin{array}{cc}
e^{i\phi} & 0 \\
0 & 1
\end{array} \right)$$
with ##\phi## as the phase.
a) Calculate the probability that detector A clicks as a function of ##\phi##
b) In practice there is always some random phase shift even in the absence of the additional element in the upper path. It comes from misalignment of beam splitters and mirrors. Assume ##\phi## is a uniformly distributed random variable. What is the probability now that detector A clicks as a function of ##\phi##?
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
a) The following vectors define the "right-moving" and "upwards-moving" photon states
$$|r> = (1,0)$$
$$|u> = (0,-1)$$
The initial right mover hits the beam splitter (defined by the matrix below) and the resulting mixed state is
$$
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\end{array} \right)
%
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
1 \\
0
\end{array} \right)
= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \big ( (1,0) + (0,-1) \big)
$$
Both beams then hit mirrors, so I apply the mirror (matrix below) to the mixed state
$$
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
0 & 1 \\
-1 & 0
\end{array} \right)
%
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
1/\sqrt{2} \\
-1/\sqrt{2}
\end{array} \right)
=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \big ( (-1,0) + (0,-1) \big)
$$
Only the top beam hits the phase shifter
$$
\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
e^{i\phi} & 0 \\
0 & 1
\end{array} \right)
%
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
1 \\
0
\end{array} \right)
= \frac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \big ( e^{i\phi},0 \big)
$$
Applying the beam-splitter to both states again yields
$$
\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\end{array} \right)
%
\left( \begin{array}{cc}
e^{i\phi} \\
1
\end{array} \right)
= \frac{-1}{2} (e^{i\phi} + 1 \ , 1 - e^{i\phi} )$$
The probability of the detector "a" clicking is thus given by
$$| \frac{1 - e^{i\phi}}{2} |^2 = \frac{1}{2}(1 - \cos\phi )$$
b) I have not formally studied probability theory, but I'm assuming that the phrase "assume ##\phi## is a uniformly distributed random variable" just means that all ##\phi##'s are equally likely to occur. I'm also assuming that this phenomenon affects both paths, and to calculate it I'd apply the phase shifter to both "u" and "r" states after they hit the first mirror.
May I know if I have applied concepts correctly? Thanks in advance.
(Spotted some errors, hence the edits)
Attachments
Last edited: