SUMMARY
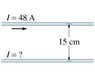
The discussion focuses on calculating the current in a suspended copper wire parallel to a current-carrying wire. The initial current in the upper wire is 48 A, and the magnetic field (B) at a distance of 15 cm is calculated using the formula μI / 2∏r, resulting in B = 4.2639 * 10^-4 T. The current in the lower wire is then determined to be 3.19 A using the relationship B(2∏r) / μ = I. An arithmetic error was identified, correcting the magnetic field to B = 6.4 * 10^-5 T.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ampère's Law
- Familiarity with magnetic fields and their calculations
- Knowledge of the properties of copper wire, including its diameter
- Basic algebra for solving equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Ampère's Law in different configurations
- Learn about the magnetic field produced by long straight conductors
- Explore the effects of wire diameter on current-carrying capacity
- Investigate the principles of magnetic suspension systems
USEFUL FOR
This discussion is beneficial for physics students, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in electromagnetic theory and applications involving current-carrying conductors.