SUMMARY
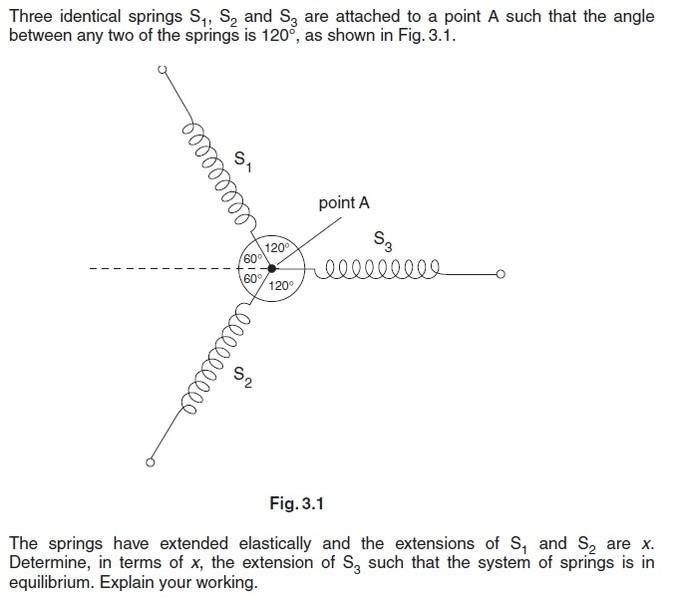
The discussion focuses on calculating the extension of identical springs using Hooke's Law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is proportional to its extension. The spring constant, denoted as k, is crucial for determining the extension when a force is applied. The problem specifically involves extending two springs by a distance x and incorporates the sine of 30 degrees, which equals 0.5, to aid in calculations. Understanding these principles is essential for solving similar physics problems effectively.
PREREQUISITES
- Hooke's Law and its applications
- Understanding of spring constants (k)
- Basic trigonometry, specifically sine values
- Concept of force and extension in springs
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation and applications of Hooke's Law
- Explore problems involving multiple springs in series and parallel
- Learn about the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration in spring systems
- Investigate real-world applications of springs in engineering and mechanics
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, educators teaching mechanics, and anyone interested in understanding the principles of spring dynamics and Hooke's Law.