Mech_LS24
- 148
- 16
- Homework Statement
- I have to calculate the deflection at the end of a beam due to a force. How do I find the moments in a beam while their are only forces applied (with pivots/hinges).
- Relevant Equations
- Sigma_bending = F*L^3 / 3EI
Theta = M*L / 3EI
Hello!
I have to calculate the deflection of a beam at at given point (C). The books says the should be a moment which plays a role in this deflection. How does this moment occur? I have drawn a FBD but couldn't find a moment? Should I divided the beam into separate parts or so? What am I missing here?
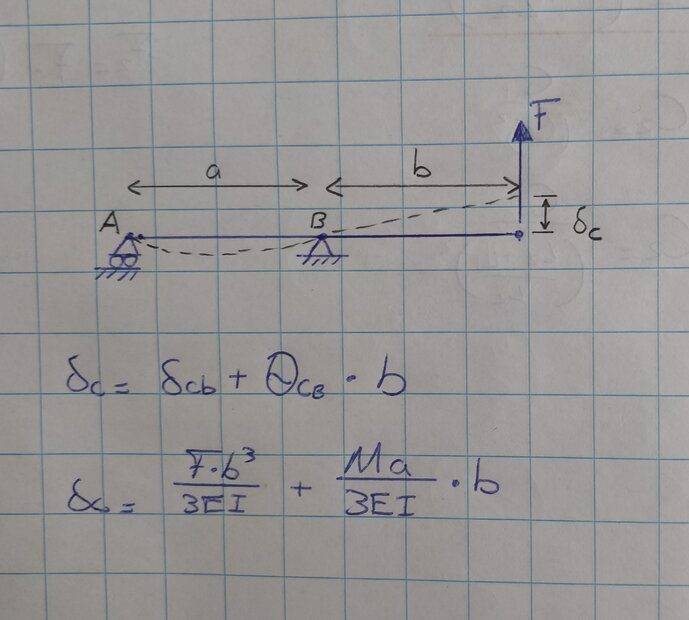
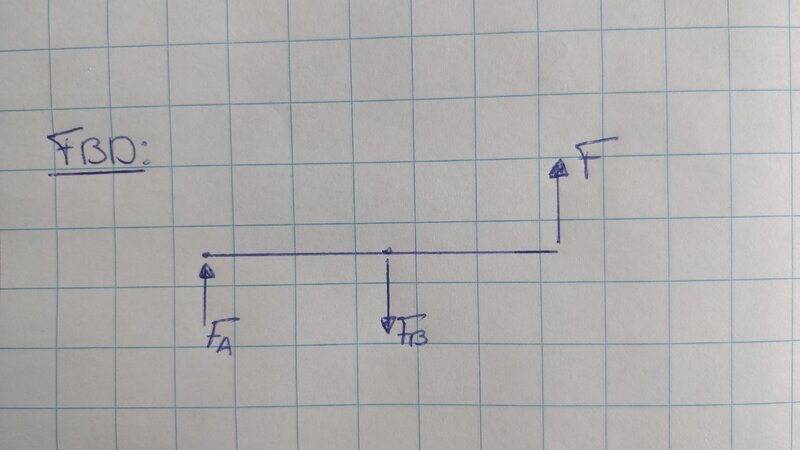
Thanks!
I have to calculate the deflection of a beam at at given point (C). The books says the should be a moment which plays a role in this deflection. How does this moment occur? I have drawn a FBD but couldn't find a moment? Should I divided the beam into separate parts or so? What am I missing here?
Thanks!