leehoom
- 5
- 0
Hi there,
I have a problem on phonon perturbation's effect on diffraction pattern.
Assume atomic planes parallel to (100) of bcc lattice is periodically perturbed by phonon.
How will diffraction pattern be modified as a result of such perturbation? Will we see any diffraction peaks in addition to those seen for a unperturbed lattice?
Thanks!
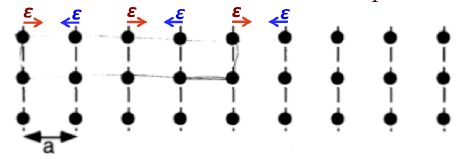
I have a problem on phonon perturbation's effect on diffraction pattern.
Assume atomic planes parallel to (100) of bcc lattice is periodically perturbed by phonon.
How will diffraction pattern be modified as a result of such perturbation? Will we see any diffraction peaks in addition to those seen for a unperturbed lattice?
Thanks!