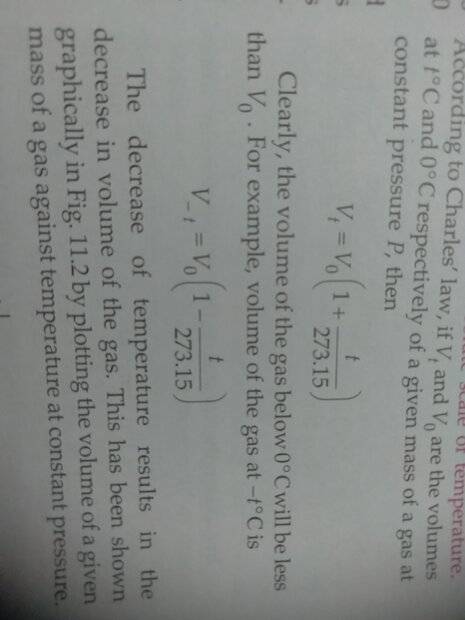SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the derivation of the Absolute Scale of Temperature as presented in SL Arora's Class 11 textbook, specifically on page 11.3 under section 11.7. The key concept discussed is Charles's Law, which states that the volume (V) of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature (T) at constant pressure. The conversion to the Absolute Scale involves adding 273.15 to the Celsius temperature, resulting in the expression (T + 273.15) for temperature in Kelvin.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Charles's Law
- Basic knowledge of temperature scales
- Familiarity with the Celsius and Kelvin temperature conversions
- Concept of gas behavior under constant pressure
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of Charles's Law in detail
- Learn about the relationship between temperature and gas volume
- Explore the implications of the Absolute Scale in thermodynamics
- Investigate other temperature scales and their conversions
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, educators teaching thermodynamics, and anyone interested in the principles of gas laws and temperature scales.