emdezla
- 11
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Calculate the input-referred thermal noise voltage of the circuit assuming lambda equal zero.
- Relevant Equations
- Both the equations and the solutions are attached
So this is a problem from the legendary Razavi book "Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits" (Specifically, it is the problem 7.7 (c)). I got the solutions online but when I try to calculate the noise expression myself, I don't arrive at the same result. Lambda is assumed zero for neglecting Ro of the transistors
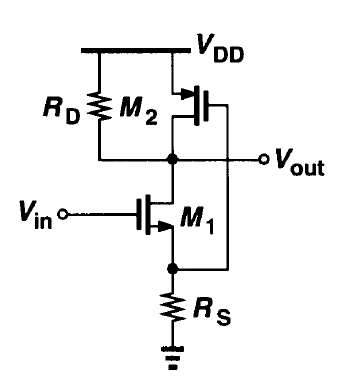
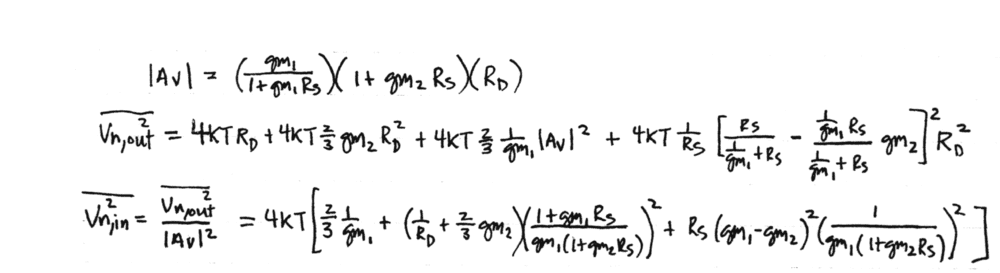
I know the circuit voltage gain Av=Vout/Vin has to be computed and I can to do that.
Then I know that every element of the circuit has to be assumed as a source of current noise. I also can do that, and for this case, we have the 4 following current noise:
I know the circuit voltage gain Av=Vout/Vin has to be computed and I can to do that.
Then I know that every element of the circuit has to be assumed as a source of current noise. I also can do that, and for this case, we have the 4 following current noise:
- Current noise from Rd = 4KT/Rd
- Current noise from M1 = 4KT*(2/3)*gm_1
- Current noise from M2 = 4KT*(2/3)*gm_2
- Current noise from RS = 4KT/Rs
- Resistance for M1 noise: if this transistor is used for amplification then R = Av/gm_1
- Resistance for M2 noise: if this transistor is used as an active load then R = Rout (output resistance of the whole circuit)
- Resistance for Rd noise: no idea, but usually is R = Rd
- Resistance for Rs noise: no idea at all