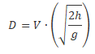SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the validity of the equation for calculating the launch velocity of a projectile from a height, specifically the expression V = \sqrt{\frac{g}{2h}}, where g is gravitational acceleration (-9.8 m/s²) and h is the height of the launch point. Participants clarify that this equation, while seemingly simplistic, incorporates a time component implicitly, as \sqrt{\frac{2h}{g}} represents the time taken for an object to fall a distance h. The conclusion is that the equation is valid for determining launch velocity when accounting for the time of flight.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic physics concepts, specifically projectile motion.
- Familiarity with gravitational acceleration and its units (m/s²).
- Knowledge of algebraic manipulation and unit analysis.
- Ability to interpret and apply kinematic equations in physics.
NEXT STEPS
- Explore the derivation of projectile motion equations, focusing on time of flight.
- Learn about the implications of air resistance on projectile motion calculations.
- Investigate the use of kinematic equations in real-world projectile motion scenarios.
- Study the relationship between horizontal and vertical components of projectile motion.
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the principles of projectile motion and the mathematical relationships involved in calculating launch velocities.
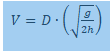 Where D=horizontal distance travelled, h=table height, and g=gravitational acceleration. Nowhere else can I find a calculation of velocity based on only two distances and GA. Everything I see has a time component or one of the velocity variables (V-i, V-f). Is this equation valid? It seems too simple. I don't care about exploring air resistance or drag coefficients, just a simple velocity at lauch calculation.
Where D=horizontal distance travelled, h=table height, and g=gravitational acceleration. Nowhere else can I find a calculation of velocity based on only two distances and GA. Everything I see has a time component or one of the velocity variables (V-i, V-f). Is this equation valid? It seems too simple. I don't care about exploring air resistance or drag coefficients, just a simple velocity at lauch calculation.