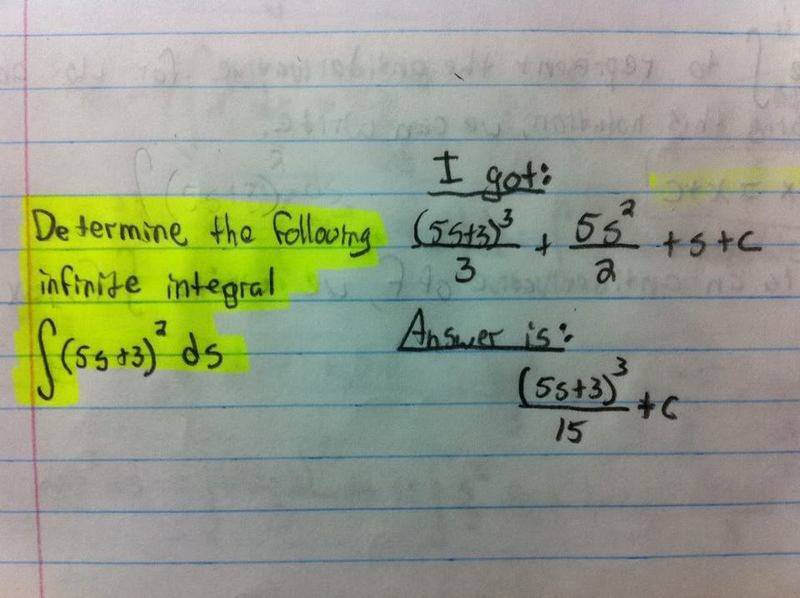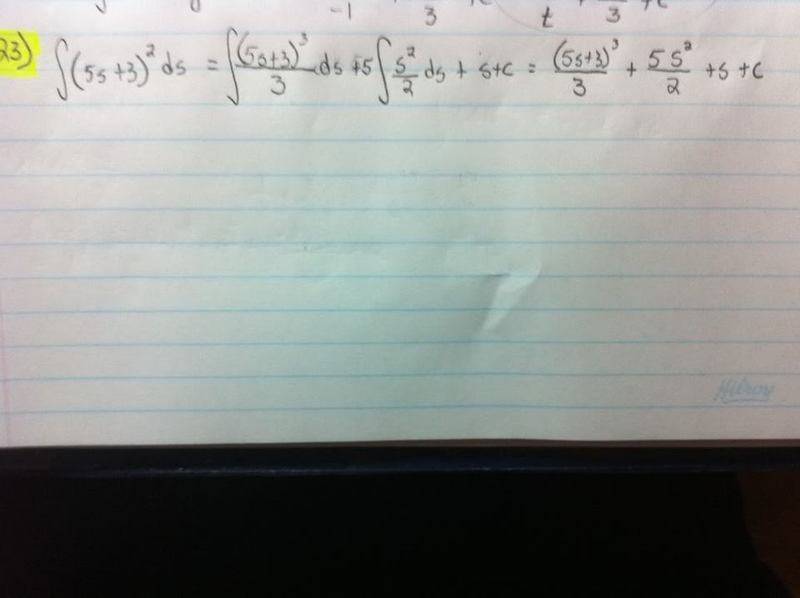SUMMARY
This discussion focuses on the concept of anti-derivatives, specifically addressing the integration of the function (5s + 3)^2. The user attempts to solve the integral using substitution, letting u = 5s + 3, which leads to the expression \(\frac{1}{5}\int u^2~du\). The conversation highlights the importance of correctly applying integration techniques and recognizing the difference between indefinite and infinite integrals. The user seeks clarification on completing the anti-derivative process from this point.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic calculus concepts, particularly differentiation and integration.
- Familiarity with substitution methods in integration.
- Knowledge of indefinite integrals and their properties.
- Ability to manipulate algebraic expressions involving polynomials.
NEXT STEPS
- Practice solving indefinite integrals using substitution techniques.
- Study the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to understand the relationship between differentiation and integration.
- Explore integration by parts as an alternative method for solving complex integrals.
- Review polynomial integration techniques, focusing on power rules and their applications.
USEFUL FOR
Students learning calculus, educators teaching integration techniques, and anyone seeking to improve their understanding of anti-derivatives and integration methods.