MigMRF
- 15
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Explain the derivation of the lorentzian line profile. Use "Laser Spectroscopy 1" By Wolfgang Demtöder pp 76-78 as inspiration
- Relevant Equations
- Fourier transform, inverse fourier transform, solution to harmonic oscilator.
First of all i tried to follow the textbook. Here they start of by modelling the atom as an harmonic oscilator:

Then they find the solution as:
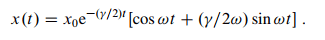
They neglect the second term as omega_0 >> gamma which also makes good sense so they end up with:
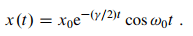
So far so good. After this they state the following:
"
Because the amplitude x.t/ of the oscillation decreases gradually, the frequency of
the emitted radiation is no longer monochromatic as it would be for an oscillation
with constant amplitude. Instead, it shows a frequency distribution related to the
function x(t) by a Fourier transformation-
The damped oscillation x(t) can be described as a superposition of monochromatic oscillations exp(i omega t) with slightly different frequencies omega and amplitudes A(omega).
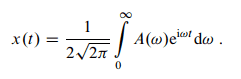
I understand that a inverse fourier transform is going on here, so that we get away from the frequency domain. And the term 1/sqrt(2 pi) is the normalization constant, which also makes good sense. But where does the 1/2 factor come from? The integral goes from 0 to infinity, and as the amplitude is a symmetric function i would expect that we'd have to multiply by two when taking the integral over the half space, not divide.
It's been some hours of trying to figure out what is going on, but without any luck. Hope that some of you can help me out understanding this step in the derivation, as the rest of it seems pretty clear.
Then they find the solution as:
They neglect the second term as omega_0 >> gamma which also makes good sense so they end up with:
So far so good. After this they state the following:
"
Because the amplitude x.t/ of the oscillation decreases gradually, the frequency of
the emitted radiation is no longer monochromatic as it would be for an oscillation
with constant amplitude. Instead, it shows a frequency distribution related to the
function x(t) by a Fourier transformation-
The damped oscillation x(t) can be described as a superposition of monochromatic oscillations exp(i omega t) with slightly different frequencies omega and amplitudes A(omega).
I understand that a inverse fourier transform is going on here, so that we get away from the frequency domain. And the term 1/sqrt(2 pi) is the normalization constant, which also makes good sense. But where does the 1/2 factor come from? The integral goes from 0 to infinity, and as the amplitude is a symmetric function i would expect that we'd have to multiply by two when taking the integral over the half space, not divide.
It's been some hours of trying to figure out what is going on, but without any luck. Hope that some of you can help me out understanding this step in the derivation, as the rest of it seems pretty clear.