Roy S Ramirez
- 24
- 4
- TL;DR
- I build a feed system for a liquid rocket injector, ran water through it, measures pressures and flow rates, and I'm not sure how to calculate the pressure drops and discharge coeffs.
Hello everybody!
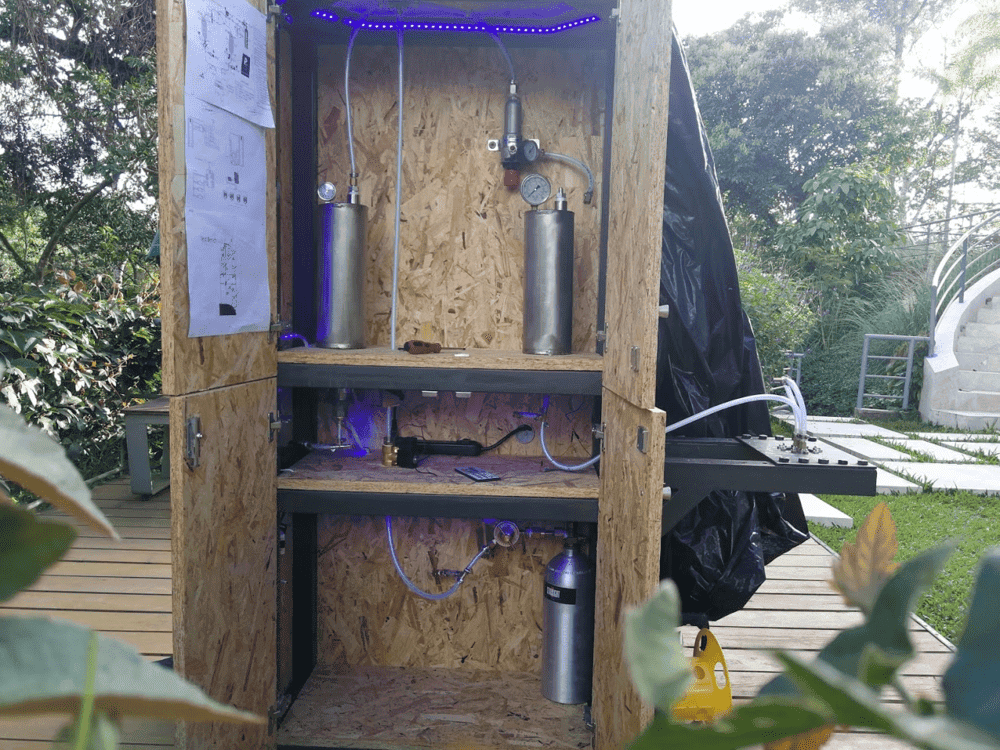
I hope you are all doing well. I built a liquid rocket injector and the following feed system:

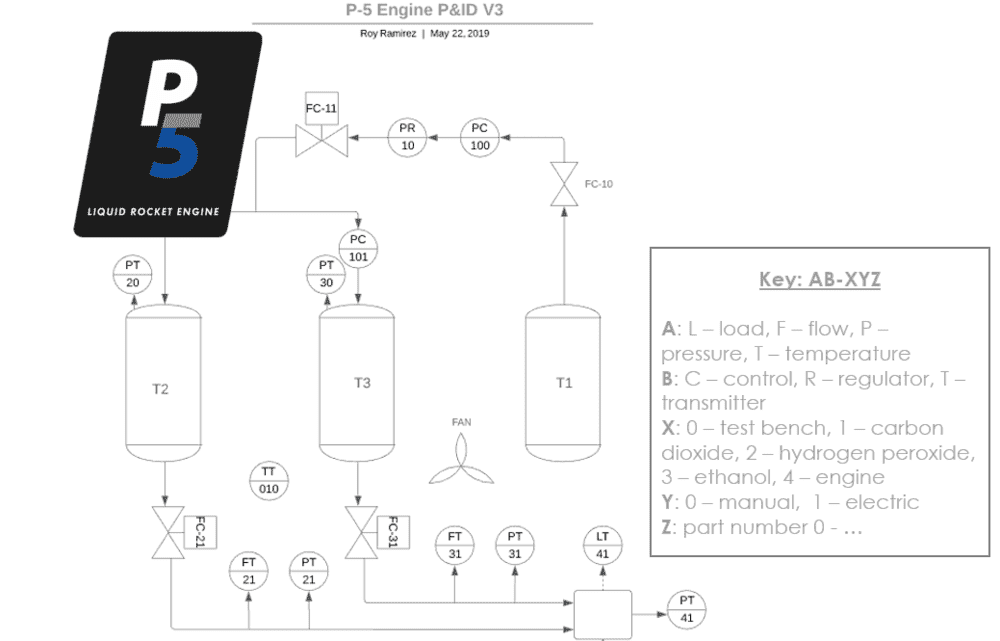
I started to do hydro-static tests (cold flows) and a program I wrote records all the data for me (except for the flow rates which I measured experimentally by collecting the water with a bucket and measuring the volume*). I know the grad students at my school use this kind of data to measure discharge coefficients, and one of them told me that for the pressure drop across the injector you just use the difference between the injection pressure (which my program records), and the atmospheric pressure. I'm not sure if this true... This a a data sample, where green is the ox line and blue is the fuel line. Both lines were tested individually, and the values plotted are in PSIA vs time, where the pressure belongs to pressure transducers PT-21 and PT-31. It is interesting to note that the PT's spike up some seconds after opening the main valves (FC-21/FC-31) at t=4secs. Also note that PT-31 looks noisy, and this is because the device is defective but it still works fairly enough (it will be replaced).
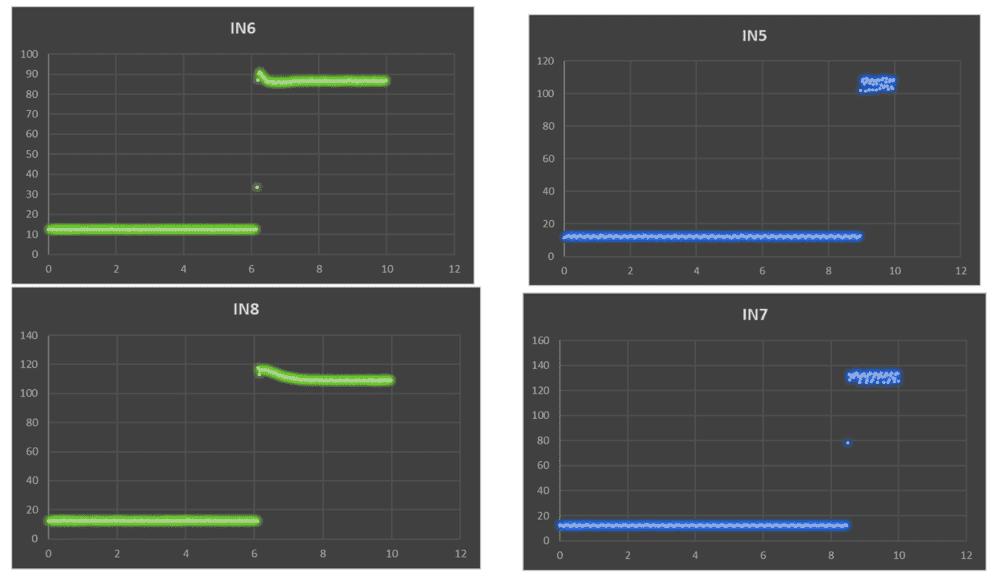
(A total of 10 individual tests were performed)
For the calculations we have the following:
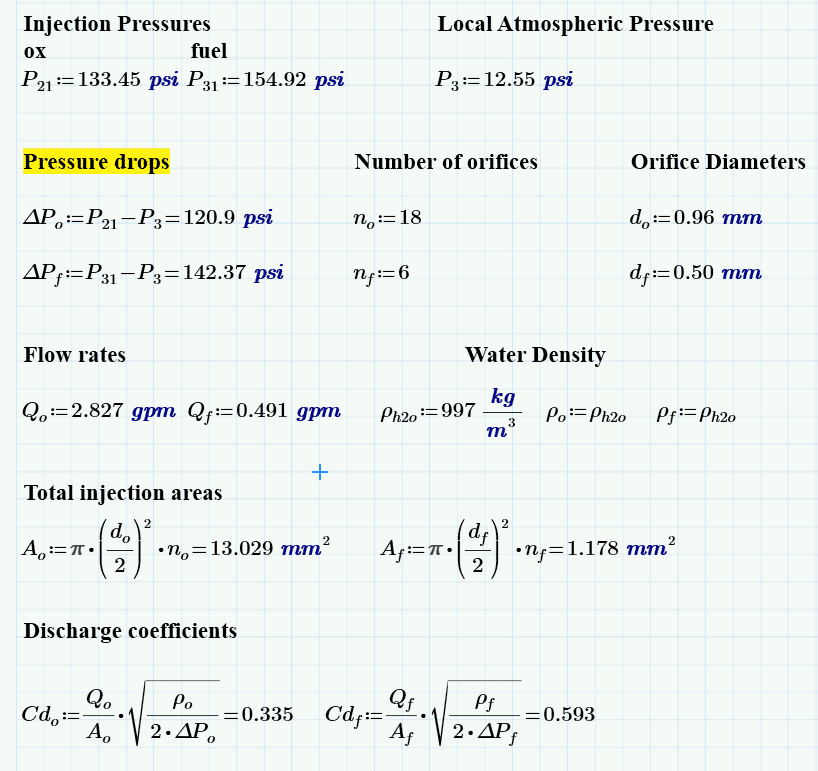
Here I vary the values of the injection pressures and the flow rates to get the Cd's. After plugging numbers I got:
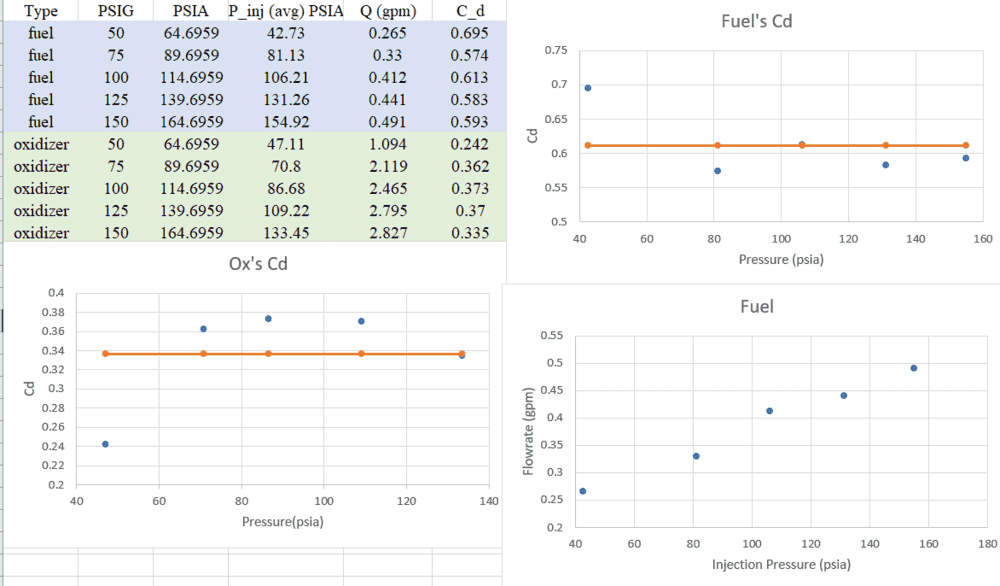 As you can see, the Cd's are varying with the injection pressure, and I thought they were supposed to be nearly fixed numbers. Also for the oxidizer line I think a Cd of 0.33 ish would be very low, wouldn't it?
As you can see, the Cd's are varying with the injection pressure, and I thought they were supposed to be nearly fixed numbers. Also for the oxidizer line I think a Cd of 0.33 ish would be very low, wouldn't it?
Thank you very much,
Roy S.
I hope you are all doing well. I built a liquid rocket injector and the following feed system:
I started to do hydro-static tests (cold flows) and a program I wrote records all the data for me (except for the flow rates which I measured experimentally by collecting the water with a bucket and measuring the volume*). I know the grad students at my school use this kind of data to measure discharge coefficients, and one of them told me that for the pressure drop across the injector you just use the difference between the injection pressure (which my program records), and the atmospheric pressure. I'm not sure if this true... This a a data sample, where green is the ox line and blue is the fuel line. Both lines were tested individually, and the values plotted are in PSIA vs time, where the pressure belongs to pressure transducers PT-21 and PT-31. It is interesting to note that the PT's spike up some seconds after opening the main valves (FC-21/FC-31) at t=4secs. Also note that PT-31 looks noisy, and this is because the device is defective but it still works fairly enough (it will be replaced).
(A total of 10 individual tests were performed)
For the calculations we have the following:
Here I vary the values of the injection pressures and the flow rates to get the Cd's. After plugging numbers I got:
Thank you very much,
Roy S.
Last edited: