- #1
milkism
- 117
- 15
- Homework Statement
- Find the surface density on the conducting surface in terms of potential either in cartesian coordinates or spherical.
- Relevant Equations
- See solution.
Problem:
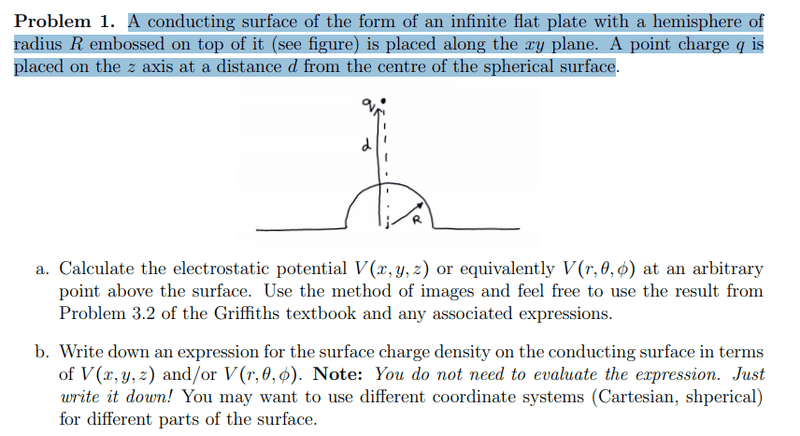
I have done part a) in spherical polar coordinates.
For part b) I thought it would be just:
$$\sigma = -\epsilon_0 \frac{\partial V}{\partial r}$$
But I got confused by "You may want to use different coordinate systems .." So I assume partial derivative w.r.t to r is the spherical part, what would the cartesian part be? I assume for the cartesian part it would be the partial derivative with respect to z, but in my solution for part a) I don't have a z-component, do I have to find the potential in Cartesian coordinates also?
I have done part a) in spherical polar coordinates.
For part b) I thought it would be just:
$$\sigma = -\epsilon_0 \frac{\partial V}{\partial r}$$
But I got confused by "You may want to use different coordinate systems .." So I assume partial derivative w.r.t to r is the spherical part, what would the cartesian part be? I assume for the cartesian part it would be the partial derivative with respect to z, but in my solution for part a) I don't have a z-component, do I have to find the potential in Cartesian coordinates also?
Last edited:
