SUMMARY
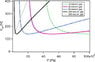
The discussion centers on calculating the optimum electrode spacing for achieving the minimum breakdown voltage of pure Neon gas at a pressure of 74762 microns. The user is operating at a voltage of 260V DC, which is above the minimum threshold. The breakdown voltage is influenced by the electric field, which is determined by the applied voltage and electrode spacing. The Paschen Curve is referenced as a critical tool for understanding the relationship between breakdown voltage, pressure, and electrode spacing.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Paschen's Law and its application in gas breakdown voltage
- Familiarity with electric field calculations in Volts per meter
- Knowledge of the Paschen Curve and its significance in electrical engineering
- Basic principles of gas physics, specifically regarding Neon
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Paschen Curve for different gases and pressures
- Learn how to calculate electric field strength and breakdown voltage
- Explore the effects of varying electrode spacing on breakdown voltage
- Investigate practical applications of Neon in high-voltage systems
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, physicists, and researchers involved in high-voltage applications, particularly those working with gas discharge phenomena and breakdown voltage calculations.