LCSphysicist
- 644
- 163
- Homework Statement
- .
- Relevant Equations
- .
I was doing the exercise as follows:
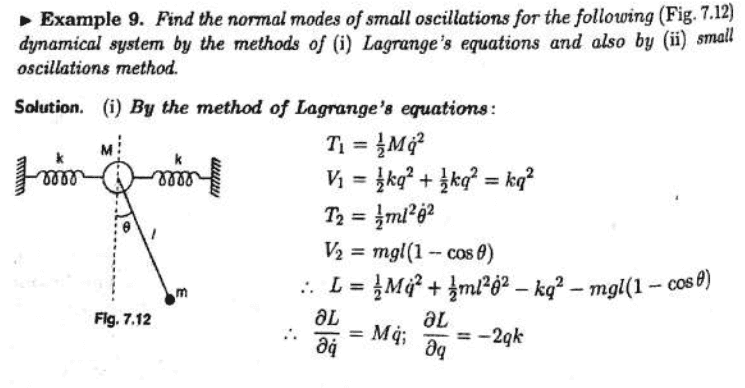
I am not sure if you agree with me, but i disagree with the solution given.
I was expecting that the kinect energy of the mass ##m## (##T_2##) should be $$T_2 = \frac{m((\dot q+lcos(\theta)\dot \theta)^2 + (lsin(\theta) \dot \theta)^2)}{2}$$
I could be wrong, of course, but i have tried to figure out my error and was not able to discover. So my guess is that the solution can be wrong.
I am not sure if you agree with me, but i disagree with the solution given.
I was expecting that the kinect energy of the mass ##m## (##T_2##) should be $$T_2 = \frac{m((\dot q+lcos(\theta)\dot \theta)^2 + (lsin(\theta) \dot \theta)^2)}{2}$$
I could be wrong, of course, but i have tried to figure out my error and was not able to discover. So my guess is that the solution can be wrong.