SUMMARY
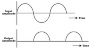
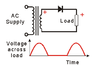
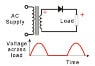
The discussion centers on the output characteristics of a half wave rectifier, which utilizes a single diode to convert AC to DC. Participants clarify that during the negative half cycle, the diode is reverse biased, preventing current flow, and thus the output is not AC but rather a pulsed DC. The conversation emphasizes that the load resistor only experiences current during the positive half cycle when the diode conducts, leading to a pulsed voltage across it. Misunderstandings about current flow in the secondary winding of the transformer are addressed, reinforcing the concept of complete circuit paths for current flow.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of half wave rectifier circuits
- Knowledge of diode operation and biasing
- Familiarity with transformer secondary winding behavior
- Basic principles of AC and DC voltage
NEXT STEPS
- Study the waveform characteristics of half wave rectification
- Learn about smoothing capacitors in power supply design
- Explore the differences between AC and pulsed DC outputs
- Investigate complete circuit paths and their importance in electronics
USEFUL FOR
Electronics students, circuit designers, and anyone interested in understanding rectification processes and their implications in power supply design.