SUMMARY
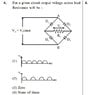
The discussion centers on analyzing the output voltage in a circuit with diodes D1, D2, D3, and D4 under forward bias conditions. Participants conclude that the output voltage Vo will be zero due to the cancellation of current paths through matched diodes, despite the potential for different resistance values among the diodes. The conversation highlights the assumption of ideal diode behavior, where forward-biased diodes are treated as short circuits, and emphasizes the importance of understanding the diode equation for real-world applications.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of diode behavior in circuits, specifically forward and reverse bias conditions.
- Familiarity with the Shockley diode equation and its implications on voltage drop.
- Basic knowledge of circuit analysis techniques, including current path evaluation.
- Awareness of ideal vs. non-ideal diode characteristics and their impact on circuit performance.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Shockley diode equation for a deeper understanding of diode voltage characteristics.
- Learn about the differences between ideal and real diodes, including the effects of forward voltage drop.
- Research full-wave rectifier configurations and their operational principles.
- Explore practical circuit analysis techniques for evaluating complex diode circuits.
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone interested in understanding diode behavior in electronic circuits.