SUMMARY
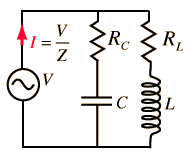
The discussion centers on the application of the general impedance equation for parallel RLC circuits, specifically when resistors are not directly in parallel with other components. The user inquires about substituting two resistors with an equivalent resistance and presents equations for the circuit's behavior. The circuit is an AC circuit, necessitating the use of reactance for capacitors (Xc = 1/ωC) and inductors (Xl = ωL) to derive the overall impedance from the two parallel arms: (Rc and C in series) and (Rl and L in series).
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of RLC circuit configurations
- Knowledge of AC circuit analysis
- Familiarity with reactance calculations for capacitors and inductors
- Proficiency in using impedance equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the general impedance equation for RLC circuits
- Learn about series and parallel combinations of resistors, capacitors, and inductors
- Explore the concept of equivalent resistance in complex circuits
- Investigate the impact of frequency on reactance in AC circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and students studying AC circuit theory who are looking to deepen their understanding of RLC circuit behavior and impedance calculations.