Frank Coutinho
- 4
- 0
Hello, I'm a very slow learner! I try to understand every piece of the information that is given. And recently I was solving some problems involving symmetrical components and I couldn't figure this one out:
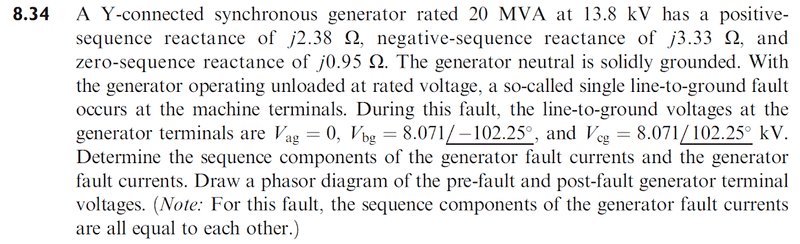
-The neutral is solidly grounded.
-Phase B and C are open.
-You're shorting Phase A trough a zero impedance.
My question is:
How the he$£ those phase voltages become that?
I mean, I would expect Phase A and B voltage (Vag, Vbg) to be equal to before the fault, since it is open circuit and the neutral is solidly grounded.
Plus, a zero-sequence and negative-sequence voltage components are present in that. Wasn't the generator suppose to only supply positive-sequence voltage?
Despite all that, I'm sure the exercise is correct, but I do not know why is that.
Hope you can help me :) !
-The neutral is solidly grounded.
-Phase B and C are open.
-You're shorting Phase A trough a zero impedance.
My question is:
How the he$£ those phase voltages become that?
I mean, I would expect Phase A and B voltage (Vag, Vbg) to be equal to before the fault, since it is open circuit and the neutral is solidly grounded.
Plus, a zero-sequence and negative-sequence voltage components are present in that. Wasn't the generator suppose to only supply positive-sequence voltage?
Despite all that, I'm sure the exercise is correct, but I do not know why is that.
Hope you can help me :) !