PokemonMaster
- 9
- 0
Homework Statement
I have this homework question and was able to set up the free body diagrams for the two blocks but got stuck forming the equations in part a. Please help if you can and give explanations - I want to understand the concept for my test coming up.
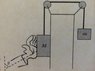
A block with mass M is pushed with a force F0 at an angle theta against a frictionless wall. It is connected to another hanging block with mass m by an ideal string and pulleys.
a. Apply Newton's Law in each direction for the two blocks to find 4 equations using the symbols given above.
b. Find an expression for the acceleration of m (the hanging block).
c. What does your answer in part b predict for the acceleration "a" if the hand stops pushing? Does this make sense?
d. What is the acceleration "a" of m if theta = 23.5 degrees, m = 3.2 kg, M = 2.1 , and F0 = 4.9 N?
Homework Equations
Fnet = ma
FG = mg
The Attempt at a Solution
a. *a1 = acceleration of block M a2 = acceleration of block m
For M
x: Fnet = 0 y: Mg - T - F0(cos theta) = Ma1
For m
x: Fnet = 0 y: T - mg = ma2
b. a2 = (Mg - F0 cos theta - Ma1 - mg) / m
* I think something went wrong here *
**** Is the acceleration of block M and m different or the same? I cannot figure that one out.
Is it perhaps that their accelerations are different with the hand present and the same with the hand not present?
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--> I could not solve c or d because I don't know if "a" is the acceleration of block M or m or if their accelerations are equal.