- #1
russguk
- 2
- 0
Hi,
This is probably an easy answer but I can't get my head round it! If I have a test rig that measures pressure differential in a test chamber at a set flow rate, how do I calculate what the pressure differential should be if I put an orfice plate in with a certain size diameter hole in the test chamber? I've attached a basic diagram of how the rig works.
Whilst using this test rig I've been obtaining some questionable results and wanted to verify that everything was as it should be with the rig. Therefore my thought was to set the rig with a flow rate of, say, 20 litres/second with an empty test chamber (closed obviously) and zero the PD meter. Then insert an orifice plate with a restriction hole in it and adjust the flow rate back to 20 litres per second and see if the PD meter reads approx the calculated value.
Could anybody please help me with this? Would be very much appreciated :)
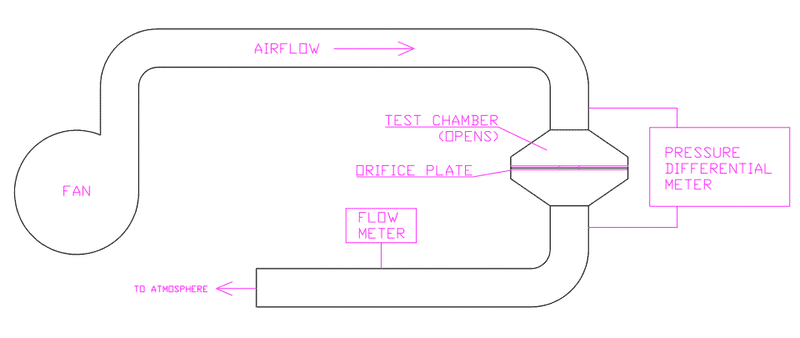
This is probably an easy answer but I can't get my head round it! If I have a test rig that measures pressure differential in a test chamber at a set flow rate, how do I calculate what the pressure differential should be if I put an orfice plate in with a certain size diameter hole in the test chamber? I've attached a basic diagram of how the rig works.
Whilst using this test rig I've been obtaining some questionable results and wanted to verify that everything was as it should be with the rig. Therefore my thought was to set the rig with a flow rate of, say, 20 litres/second with an empty test chamber (closed obviously) and zero the PD meter. Then insert an orifice plate with a restriction hole in it and adjust the flow rate back to 20 litres per second and see if the PD meter reads approx the calculated value.
Could anybody please help me with this? Would be very much appreciated :)