Homework Help Overview
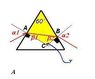
The discussion revolves around the behavior of light as it passes through an equilateral triangle prism made of crown glass, specifically focusing on the range of refraction angles when light exits into air. The original poster presents a scenario involving an angle of incidence of 55 degrees and seeks to understand the implications of this angle in relation to the prism's properties and the refraction of light.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning, Problem interpretation, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants explore the relevance of the equation provided and question the meaning of the angle of incidence and the angle of minimum deviation. There is discussion about applying Snell's law to determine angles of refraction and the challenges in calculating the angle of exit from the prism.
Discussion Status
Participants are actively engaging with the problem, sharing attempts and clarifying concepts. Some have made drawings to aid their understanding, while others express confusion about specific angles and the application of Snell's law. Guidance has been offered regarding the relationships between angles within the prism and the need to calculate multiple angles of refraction.
Contextual Notes
There are indications of uncertainty regarding the values of certain angles and the implications of the given angle of incidence. Participants are navigating through the complexities of the problem without a clear consensus on the correct approach or solution.