callekula
- 3
- 0
Hi,
I have a question regarding a pendulum and it's motion/momentum given the axis it moves around.
In the below picture, there are two version of a pendulum with a weight at the bottom. It moves in and out of the screen, around an axis resting on two nails (red). My question is, how does the distance (x and y) of the axis affect the motion, if we neglect the weight of the horisontal bar? Will the x-version move for a longer period of time, if the pendulum is released from the same position as the other version? Or is there no difference?
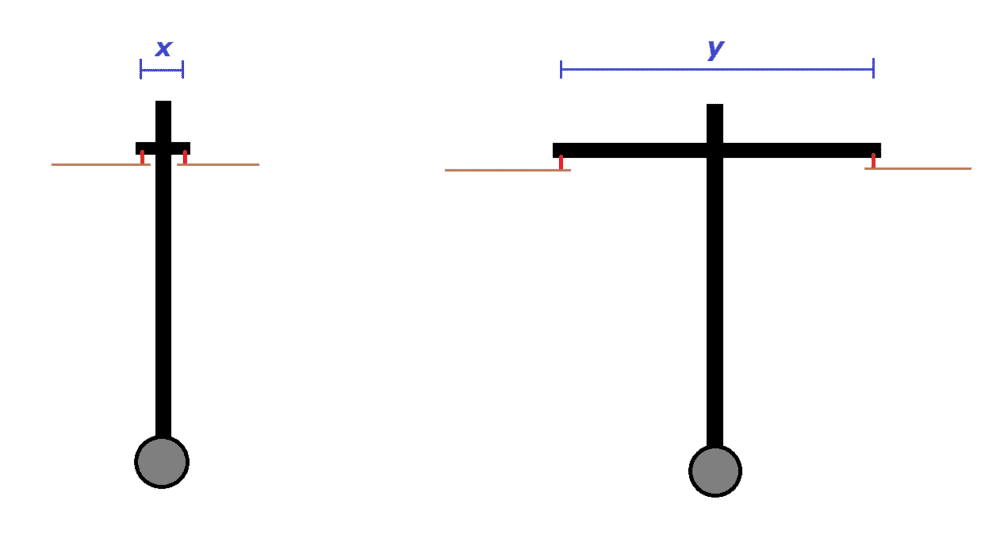
I have a question regarding a pendulum and it's motion/momentum given the axis it moves around.
In the below picture, there are two version of a pendulum with a weight at the bottom. It moves in and out of the screen, around an axis resting on two nails (red). My question is, how does the distance (x and y) of the axis affect the motion, if we neglect the weight of the horisontal bar? Will the x-version move for a longer period of time, if the pendulum is released from the same position as the other version? Or is there no difference?
 !
!