sams
Gold Member
- 84
- 2
I would really appreciate if someone could advise me whether the system below is a scleronomic or a rheonomic mechanical system, or a mix of both. If we consider the first pendulum, the constraint is fixed which leads to a scleronomous case while the constraint of the second pendulum is not fixed (varies with time) which leads to a rheonomous case.
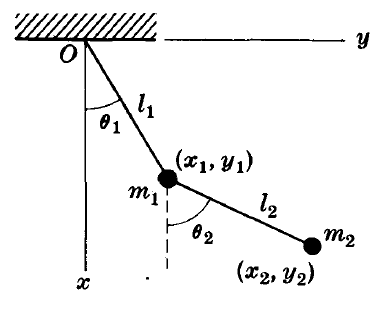
Any advice is much appreciated.
Any advice is much appreciated.