Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the necessary counterweight for a pole stand with an object hanging from it, focusing on torque and balance. Participants explore the implications of different configurations of counterweights and the effects of the pole's mass on stability, including the ability to rotate an object around the pole without flipping it.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant suggests that the problem is a simple torque calculation and proposes mapping all mass onto a horizontal plane, assuming a rigid pole frame with no mass.
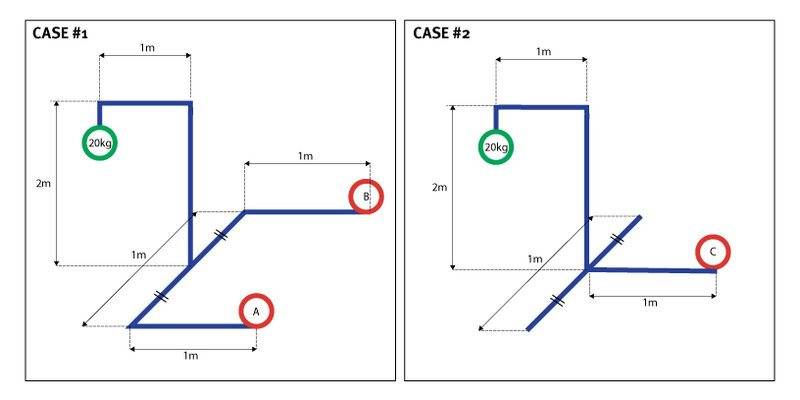
- Another participant questions the scenario when the pole frame has mass, providing specific weights for various components and inquiring about the stability of different counterweight configurations.
- A later reply emphasizes the importance of drawing a plan view to identify centers of mass and fulcrum lines, suggesting that static balance calculations should consider potential overbalance during rotation.
- Concerns are raised about the stability of the proposed cases under different angles of rotation, with one participant expressing doubt about the effectiveness of Case #2 compared to Case #1.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the effectiveness of the counterweight configurations or the implications of the pole's mass. Multiple competing views remain regarding the stability of the setups under different conditions.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the need for assumptions about the rigidity of the pole and the distribution of mass, as well as the potential for dynamic effects when the object is rotated. Specific calculations and torque values are not provided, leaving some mathematical steps unresolved.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be useful for individuals interested in mechanics, particularly those dealing with torque, balance, and stability in physical systems involving counterweights.