Discussion Overview
This discussion revolves around the measurement of the speed of light from different reference frames, particularly in the context of special relativity. Participants explore the implications of measuring light speed from a moving car and the effects of relativistic principles such as time dilation and length contraction.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant suggests that a person in a moving car would measure the speed of light as c, while a stationary observer would also measure it as c, raising questions about whether light slows down relative to the car.
- Another participant asserts that light does not slow down and maintains a speed of c in all frames, attributing differences in perceived speed to the relative motion of the car and the observer.
- A participant proposes a method for measuring light speed using a reflector and calibrated distances, but another challenges the feasibility of this method due to relativistic effects.
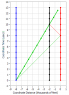
- One participant introduces a spacetime diagram to illustrate the effects of time dilation and how measurements can lead to incorrect conclusions about light speed.
- Another participant emphasizes the importance of considering relativistic effects, such as length contraction, when making measurements and understanding the implications of the relativistic velocity addition law.
- Some participants reference external resources, such as Wikipedia, to explain concepts related to special relativity, including the Lorentz transformation and its implications for the constancy of light speed.
- There is a discussion about the mathematical representation of light speed in different frames, with one participant providing algebraic reasoning to support the constancy of light speed under Lorentz transformations.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on how to interpret measurements of light speed from various frames. While some assert that light speed remains constant, others question the implications of this constancy in practical measurement scenarios. The discussion remains unresolved with multiple competing perspectives.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight limitations in understanding due to the complexity of relativistic effects, such as time dilation and length contraction, which may not be intuitive in classical terms. There are also references to the need for a solid foundation in special relativity to fully grasp the implications of the discussion.