rabbahs
- 16
- 0
Dear Forum members,
I have a bit confusion about the "Specific Heat at constant pressure".
Normally it only varies with the temperature (As given by many book at their Appendixs). But these values are only given at 1 atm pressure and with a wide range of temperature. Most of the books also specify the polynomial related to the specific heat (that only change with temperature, because pressure is held fixed at 1 atm).
My question is that what happen to Cp when the pressure increase from 1 atm to 5 atm at constant temperature. is Cp increase with increase or decrease of pressure ??
I know that its sounds bit odd that asking for Cp (which is indeed sp. heat at CONSTANT PRESSURE)
is there any polynomial which describe the change of Cp with both pressure and temperature ?
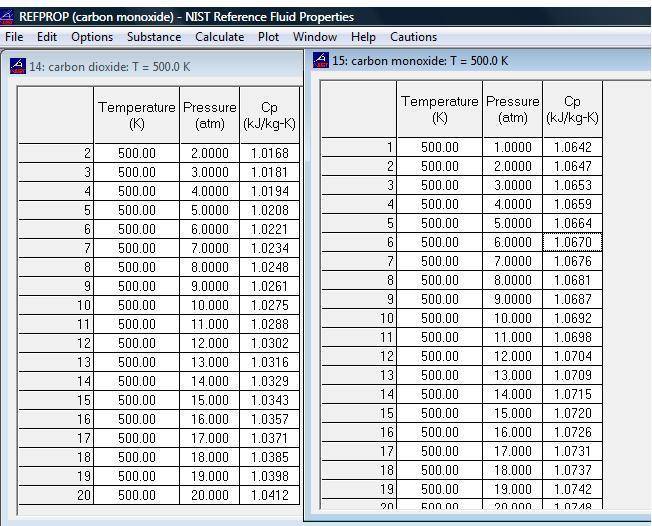
Please also view the attached file which clearly shows that Cp is changing with pressure.
I want to know that polynomial having both temperature and pressure.
Thanks a lot
I have a bit confusion about the "Specific Heat at constant pressure".
Normally it only varies with the temperature (As given by many book at their Appendixs). But these values are only given at 1 atm pressure and with a wide range of temperature. Most of the books also specify the polynomial related to the specific heat (that only change with temperature, because pressure is held fixed at 1 atm).
My question is that what happen to Cp when the pressure increase from 1 atm to 5 atm at constant temperature. is Cp increase with increase or decrease of pressure ??
I know that its sounds bit odd that asking for Cp (which is indeed sp. heat at CONSTANT PRESSURE)
is there any polynomial which describe the change of Cp with both pressure and temperature ?
Please also view the attached file which clearly shows that Cp is changing with pressure.
I want to know that polynomial having both temperature and pressure.
Thanks a lot