Litcyb
- 34
- 0
Homework Statement
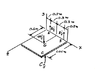
An opening in a floor is covered by a 1×1.2-m sheet of plywood of mass 18 kg. The sheet is hinged at A and B and is maintained in a position slightly above the floor by a small block C. Determine the vertical component of the reaction (a) at A, (b) at B, (c) at C.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I know how to approach this problem, however, I am just a bit confused on how to set up my F.B.D. i attached the correct f.b.d for this problem . My question is, how come if we take the moment about point A, we only have a reaction force in the j direction at support B?